Welcome Back!
In the previous blog we discussed till RTEP creation which is needed for cross-site communication.
Today we will be creating a stretched segment across two physical sites & will examine the MAC learning of VMs situated at two different sites, as well as East-West packet flows between 2 VMs residing on two different sites.
We will be discussing below topology today.
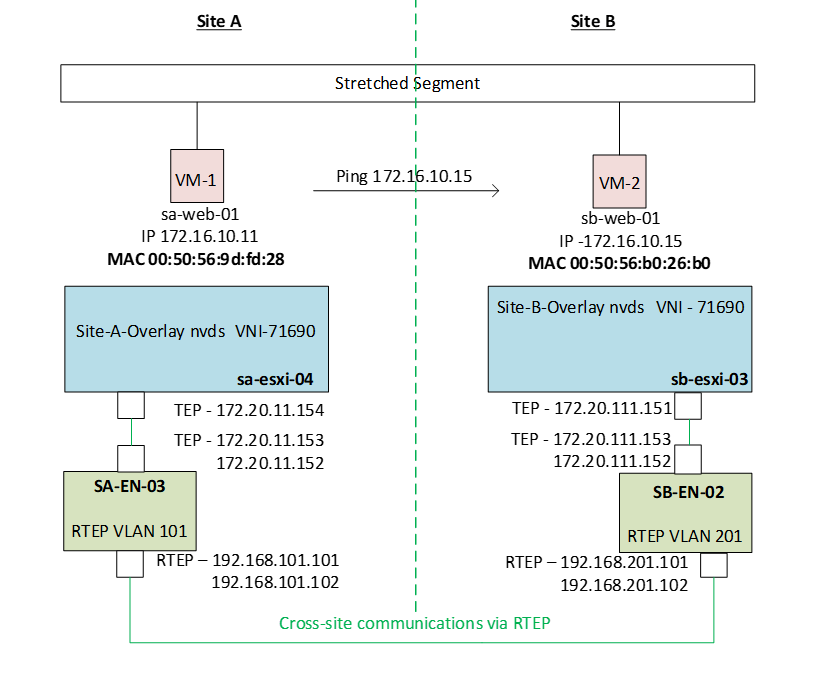
| Inventory | Site-A | Site-B |
| ESX running VM1 | sa-esxi-04 | sb-esxi-03 |
| VM Name | sa-web-01 | sb-web-01 |
| VM IP | 172.16.10.11 | 172.16.10.15 |
| VM MAC | 00:50:56:9d:fd:28 | 00:50:56:b0:26:b0 |
| Edge Node Involved | SA-EN-03 | SB-EN-02 |
| NSX Manager | sa-nsxmgr-01 | sb-nsxmgr-01 |
| RTEP | 192.168.101.101 192.168.101.102 | 192.168.201.101 192.168.201.102 |
As we discussed in our early blogs, that we don’t really create a stretch segment in NSX, but we create stretch gateways and segments simply takes the span of the gateway (T1 /T0) it relates to.
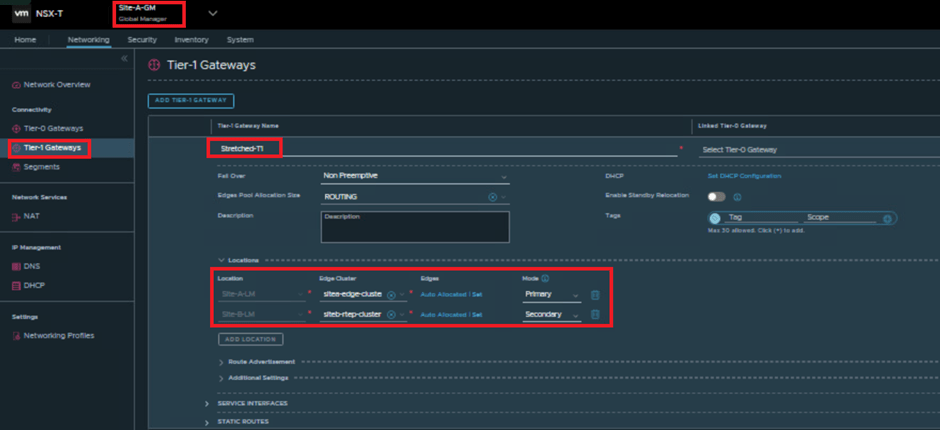
So, lets create a stretch Tier-1 with required details like.
| Name | Stretched-T1 |
| Failover Status | Non-Pre-emptive |
| Primary Location | Site-A |
| Secondary Location | Site-B |
Create a segment & connect with this stretched-T1, we see automatically this segment is stretched to 2 locations which it has inherited from the gateway it is attached.
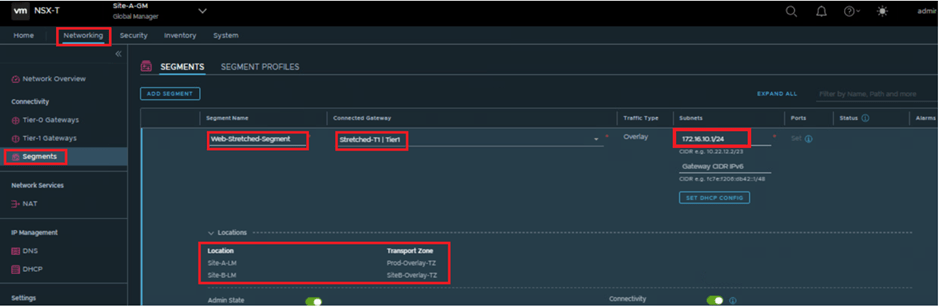
Once the segment is created, we attached VM1 (present at Site-A) & VM2 (present at Site-b) with it, which looks like below diagram.
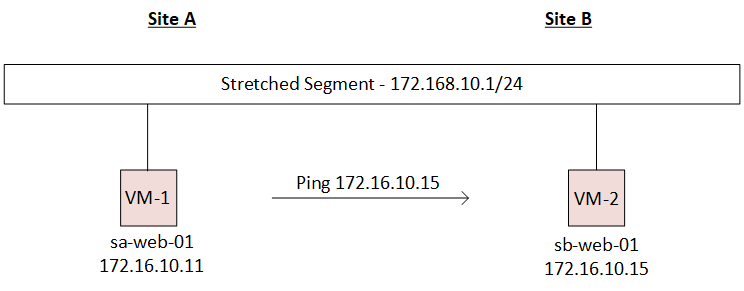
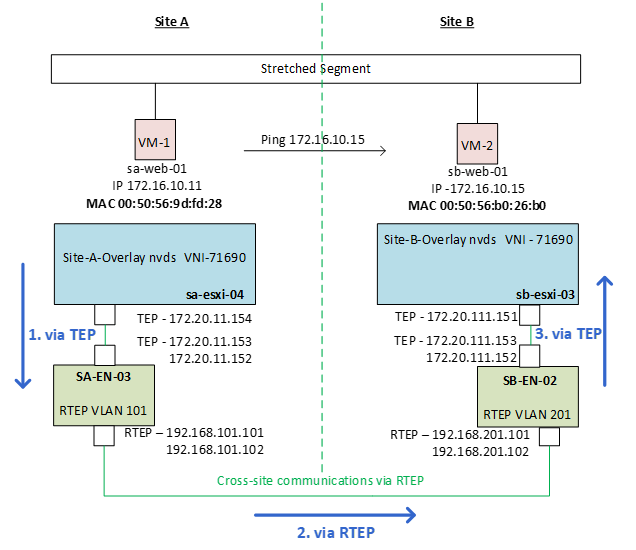
Now the major point is to understand the mac learning across sites, which involves below steps:
MAC learning steps:
1. The NSX Edge node configured with RTEPs learns the MAC address of the remote VMs connected to the stretched segment.
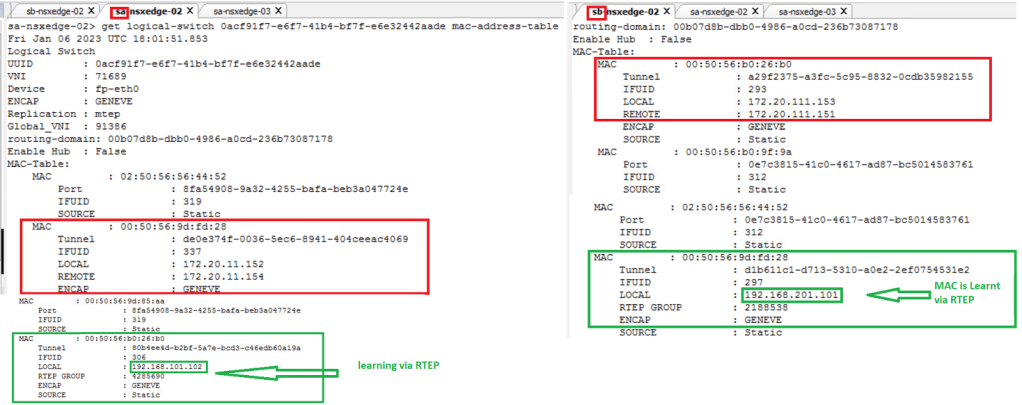
2. The NSX Edge node sends the MAC address information to the Local Manager (LM).
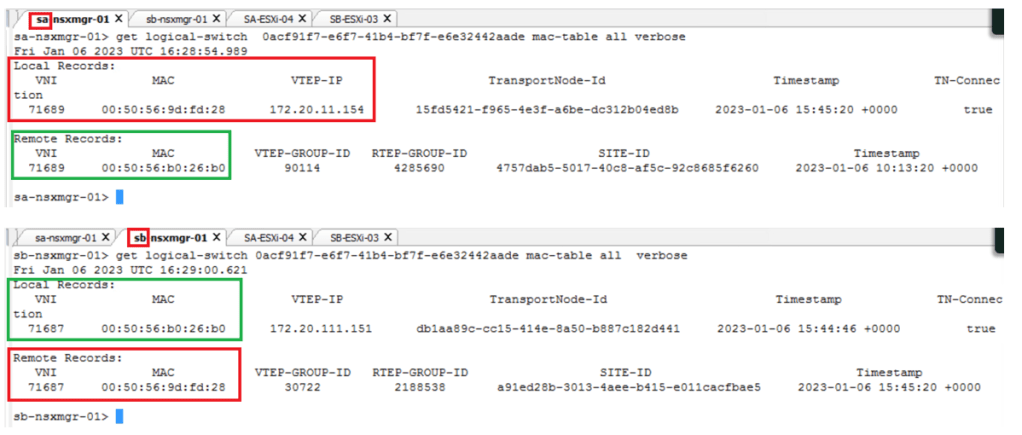
3. The LM pushes this MAC address information to the local transport node (ESXi).
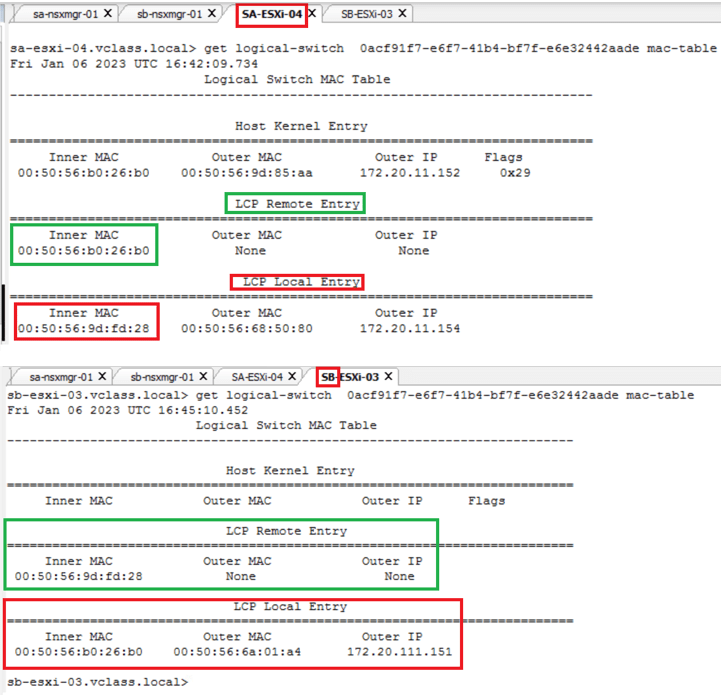
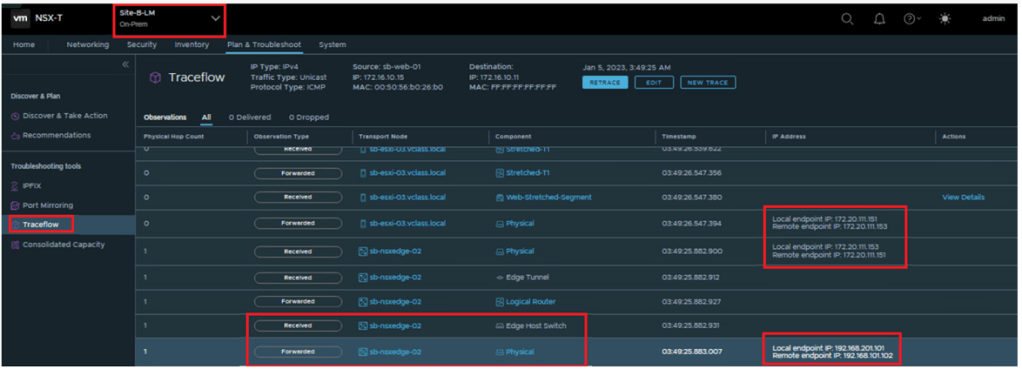
Now we have seen the actual MAC learning which is needed for East-West packet flow, we can see the packet walk with inbuilt NSX traceflow tool.
Where we will notice that Packet will leave from Site-A ESXi to Site-A Edge-node configured with RTEP towards Site-B Edge node to Site-B ESXi.
sa-web-01 > sa-esxi-04 > (via TEP) SA-EN-03 > (via RTEP) SB-EN-02 > (via TEP) sb-esxi-03 > sb-web-01
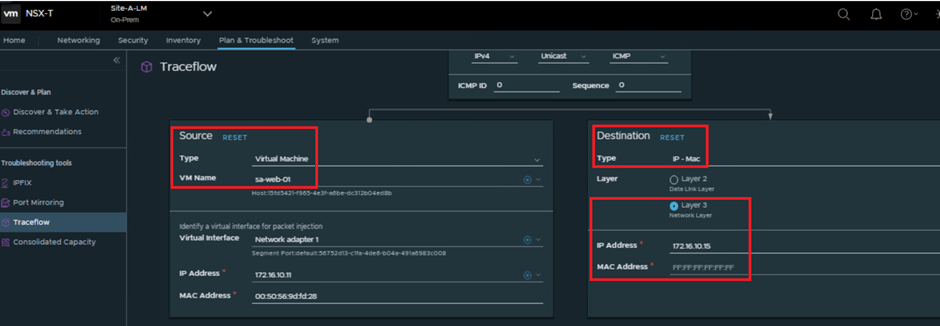
Lets examine the same via Trace-flow :
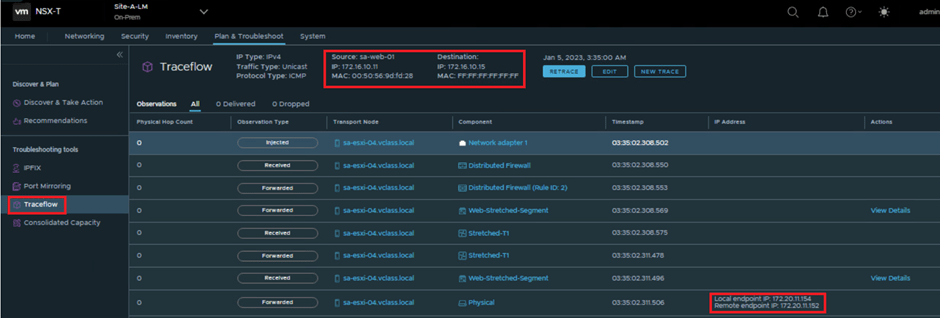
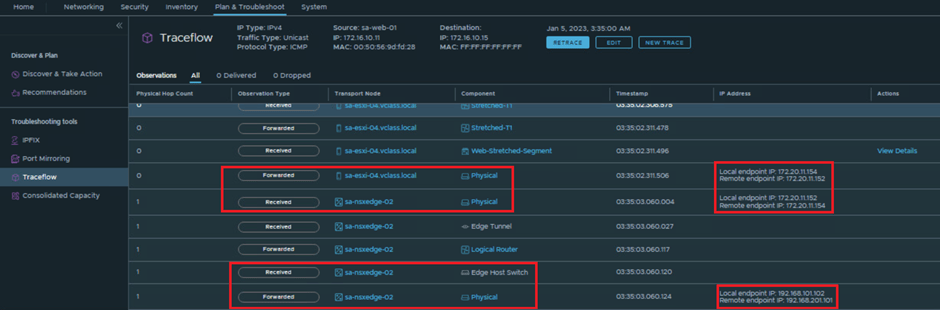
Note : Since trace-flow is only responsible for single site we will see the packet walk till edge node to Remote TEP at both sites, but now since we have examined the MAC learning from remote site we can totally relate with the packet walk.
Reverse trace flow from Site-B to Site-A.


This is it for today’s blog. We will be discussing about “North-South packet walk” in next blog, Stay tuned…
PS: Any Improvement points or suggestions are welcome.
—–Thank You—–
Prashant Pandey

